Introduction
Modern data teams are expected to do more than just deliver insights—they’re increasingly responsible for building systems that act on those insights automatically. Whether you’re enriching datasets, responding to triggers, or running structured AI workflows, automations are how you scale your impact. TrueState’s Automations system allows you to build intelligent, workflows using a drag-and-drop canvas. Each automation can combine large language models, user input, decision logic, data lookups, and external integrations. This guide walks through how to build, test, and deploy AI-powered automations in TrueState.What are Automations?
Automations in TrueState are visual workflows that let you orchestrate multiple steps into a single repeatable flow. Each automation is built from steps—units of work like:- Calling a large language model (LLM)
- Running logic or calculations
- Requesting input from a user
- Extracting data from a webpage or API
- Making decisions based on logic or AI judgment
Creating an Automation
To get started:- Visit the Automations page
- Click Create new automation
- Enter a name and description
- Click Create
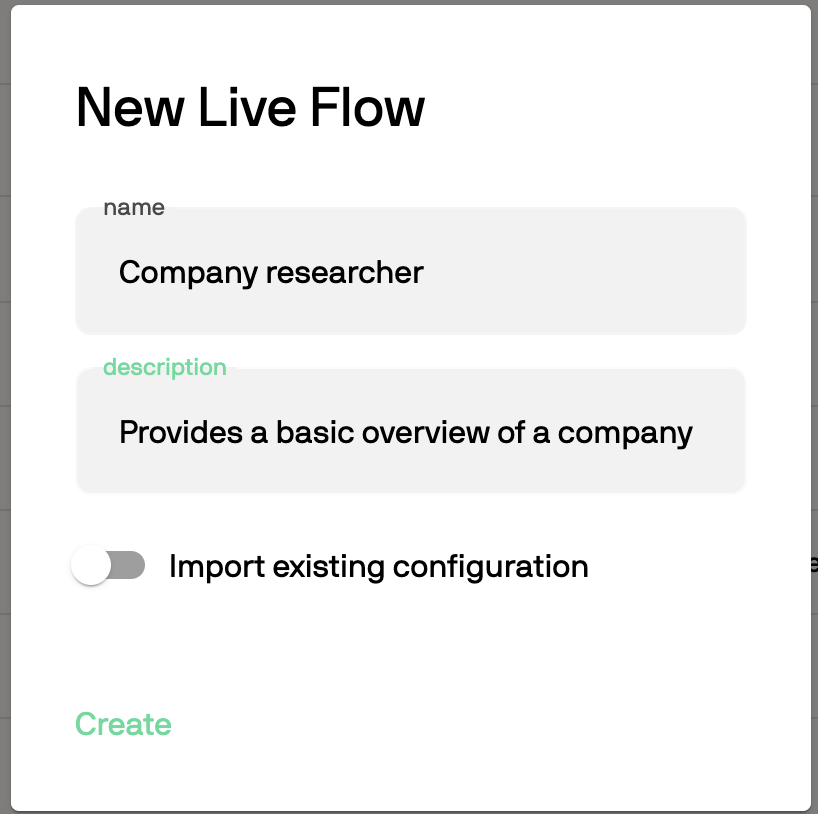
What you should expect to see when creating a new automation
Working in the Canvas
The canvas is where you design your automation by dragging steps from the sidebar into the main workspace. You can connect steps in sequence, set outputs, and pass values between them.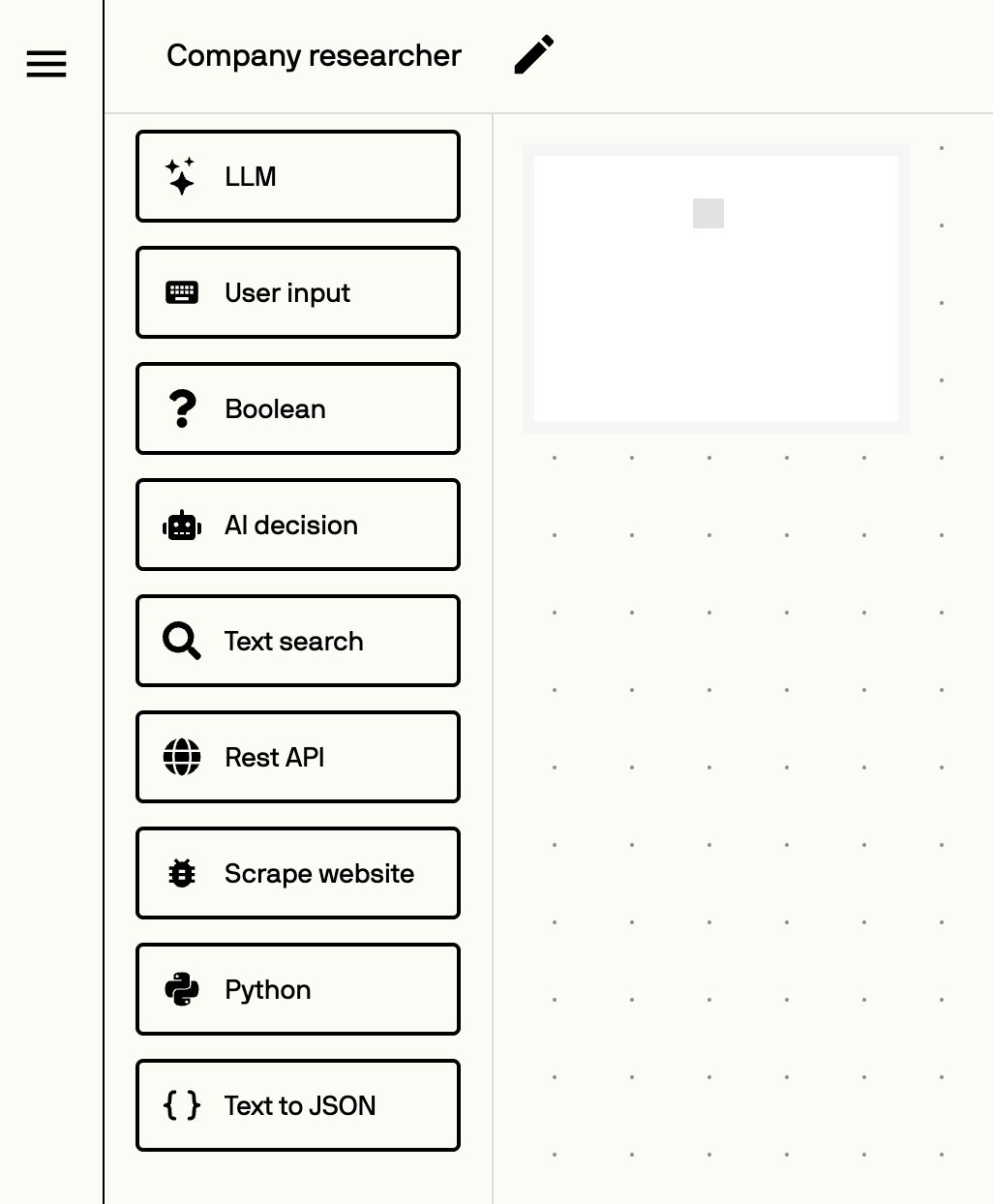
The steps menu in the automation builder
Step Types
LLM
Use a large language model to generate text, answer questions, summarise inputs, or transform unstructured data. Example: Summarise HTML into 3 bullet points.User Input
Pause the automation and request input from a human—via form, dropdown, or free text. Example: Ask a user to approve a draft response before sending it.Boolean
Route the automation using a Python expression that evaluates to true or false. Example: Check whether the input text is longer than 1000 characters.AI Decision
Use an LLM to evaluate a situation and choose a path based on instruction logic. Example: Determine if an inbound message is about pricing, support, or a product bug.Text Search
Search an indexed document or dataset and retrieve the top 10 matches. Example: Retrieve policy documents mentioning “carbon offset” for reference.Requires pre-indexing of data via the platform. See the Text Analytics guide for details.
REST API
Call a third-party REST API with GET or POST. Useful for data enrichment, lookup, or triggering external systems. Example: Fetch company data from an enrichment API using a domain name.Python
Execute a single line of Python. Ideal for string manipulation, lightweight math, or logic. Example: Clean newline characters or truncate strings before passing to an LLM.Text to JSON
Use an LLM to extract structured JSON from messy or free-form text. Example: Extractname, industry, and location from a company description block.
Example: Company Research Automation
Let’s walk through a simple automation that:- Accepts a company URL
- Scrapes the homepage
- Uses an LLM to summarise what the company does
Step 1: Add a User Input step
Prompt for the URL with the label:- Label: Company URL
- Variable: url
Step 2: Add a websraping step to scrape the site
Use the following code: Python script:- Output variable: text
Step 3: Add an LLM step
Use the following prompt: Prompt:- Output variable: summary
Step 4: Display the Result
You can optionally use another User Input step, a logging step, or a custom integration to show or export the result.Using Automations in Pipelines
Automations can be embedded inside Pipelines using the Automation step. This allows you to run an automation once per row in a dataset. Common use cases:- Summarise each customer review
- Extract entities from inbound support messages
- Generate product descriptions or structured metadata
Next Steps
- Build your first automation from the Automations page
- Chain steps together to form more advanced logic
- Embed automations into Pipelines for row-wise execution
- Trigger automations manually, via schedule, or from events

